This at-home lab test provides valuable insights into your liver and heart health, identifying potential liver damage, inflammation, and analyzing cholesterol, VLDL, and bilirubin levels.
-
10 biomarkers measured
-
CLIA-certified and CAP-accredited lab
-
Finger prick sample
-
Fasting
-
Virtual Care available
What is measured?
This test measures the following biomarker:
-
Total cholesterol
Cholesterol is a lipid that is found in the blood. It comes from food that you eat and is also manufactured in the liver. Total cholesterol is comprised of various different types of cholesterol including low-density lipoprotein (LDL), high-density lipoprotein (HDL), and very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) cholesterol. Cholesterol is a fatty substance essential for building cells and producing many hormones. When levels are elevated, excess cholesterol is deposited into the blood vessels and is associated with heart disease and stroke.
-
HDL
High density lipoprotein (HDL) is often referred to as the "good" cholesterol. It removes LDL ("bad cholesterol") from your arteries and takes it to the liver where it is metabolized or broken down into bile acids and excreted from the body in the bile. Elevated HDL is generally considered protective against heart disease and stroke, however extremely high levels can also be problematic. Low levels increase risk of heart attack and stroke due to buildup of excess LDL in the blood vessels.
-
LDL
Low density lipoprotein (LDL) is often referred to as the "bad" cholesterol. It is produced in the liver and is deposited into the tissues where it is used to build cell membranes and hormones. Elevated LDL comes from your genetics and your diet. Eating saturated and trans fats will increase LDL levels. When oxidized, LDL is deposited into the arteries where it creates plaque and contributes to heart disease and stroke. Low LDL is associated with inflammation and increased risk of cancer and mood disorders.
-
Triglycerides
Triglycerides are a type of fat found in the bloodstream. Triglycerides are produced by the body from the food we eat and are also stored in fat cells for later use as energy. While triglycerides are essential for normal body function, high levels can increase the risk of heart attack and stroke. Extremely elevated levels are associated with pancreatitis, metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes.
-
LDL/HDL ratio
The LDL/HDL ratio measures the balance between low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, or "bad" cholesterol, and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, or the "good" cholesterol. This ratio provides a more comprehensive assessment of your cardiovascular risk than individual cholesterol levels alone. A higher ratio indicates a greater risk of heart disease and stroke. Elevated LDL levels contribute to plaque buildup in the arteries while higher HDL levels help remove cholesterol from the bloodstream.
-
Cholesterol/HDL ratio
The CHOL/HDL ratio is a measurement derived from dividing the total cholesterol (CHOL) level by the high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol level. This ratio helps assess cardiovascular risk, as a higher ratio indicates a greater risk of heart disease, while a lower ratio suggests a lower risk.
-
VLDL
VLDL is a type of lipoprotein made by the liver. VLDL is composed of a protein, cholesterol and triglyceride molecule combined together. VLDL is transported to the body and blood vessels where triglycerides are removed from the VLDL leaving an LDL cholesterol molecule. At high levels, VLDL can contribute to the buildup of plaque in the arteries leading to heart disease, and stroke.
-
AST
AST is an enzyme that is mainly found in the liver, but is also found in the heart, muscles, and kidneys. When any of these organs is damaged, AST levels rise in the blood. This test enables evaluation of liver function. Elevated AST levels can indicate problems with the liver such as liver disease, infectious hepatitis or toxicity related to medications, alcohol use, or other environmental toxins.
-
ALT
ALT (alanine aminotransferase) is an enzyme primarily found in the liver and in the kidneys, heart, and muscles. It has a role in amino acid metabolism. When elevated, ALT indicates damage to the liver such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, liver cancer, or reaction to medications. Elevated ALT can also indicate damage to other tissues, though it is less common. When ALT levels are higher than AST levels, it can be used to diagnose conditions such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD).
-
Total bilirubin
Bilirubin is produced during the normal breakdown of red blood cells. Elevated levels can indicate liver disease, blockage of the bile duct, hemolytic anemia (rapid breakdown of red blood cells), or newborn jaundice. There are two types of bilirubin including direct (conjugated) bilirubin, which has been processed by the liver, and indirect (unconjugated) bilirubin, which has not yet reached the liver for processing. Total bilirubin is a measure of both direct and indirect bilirubin combined.
Who should take this test?
This test is suitable for:
- Men or women age 18+ with chronic liver disease
- Individuals with a history of hepatitis or fatty liver disease
- Those experiencing symptoms such as yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice), persistent abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, fatigue, and unexplained weight loss
- People taking medications that can affect the liver, where the doctor will determine the frequency of tests (ranging from monthly to every 6 months) to closely monitor and adjust treatment accordingly
How to test?
Before you begin:
- Fast overnight for 12 hours and take the test in the morning.
- When you wake up, drink 12oz. of water and collect your blood sample 1 hour later.
- Avoid smoking for 1 full hour before collecting your blood sample.
- Wash your hands with soap in warm water, and then rub them together.
- Do some light exercise, like jumping jacks, to increase blood circulation.
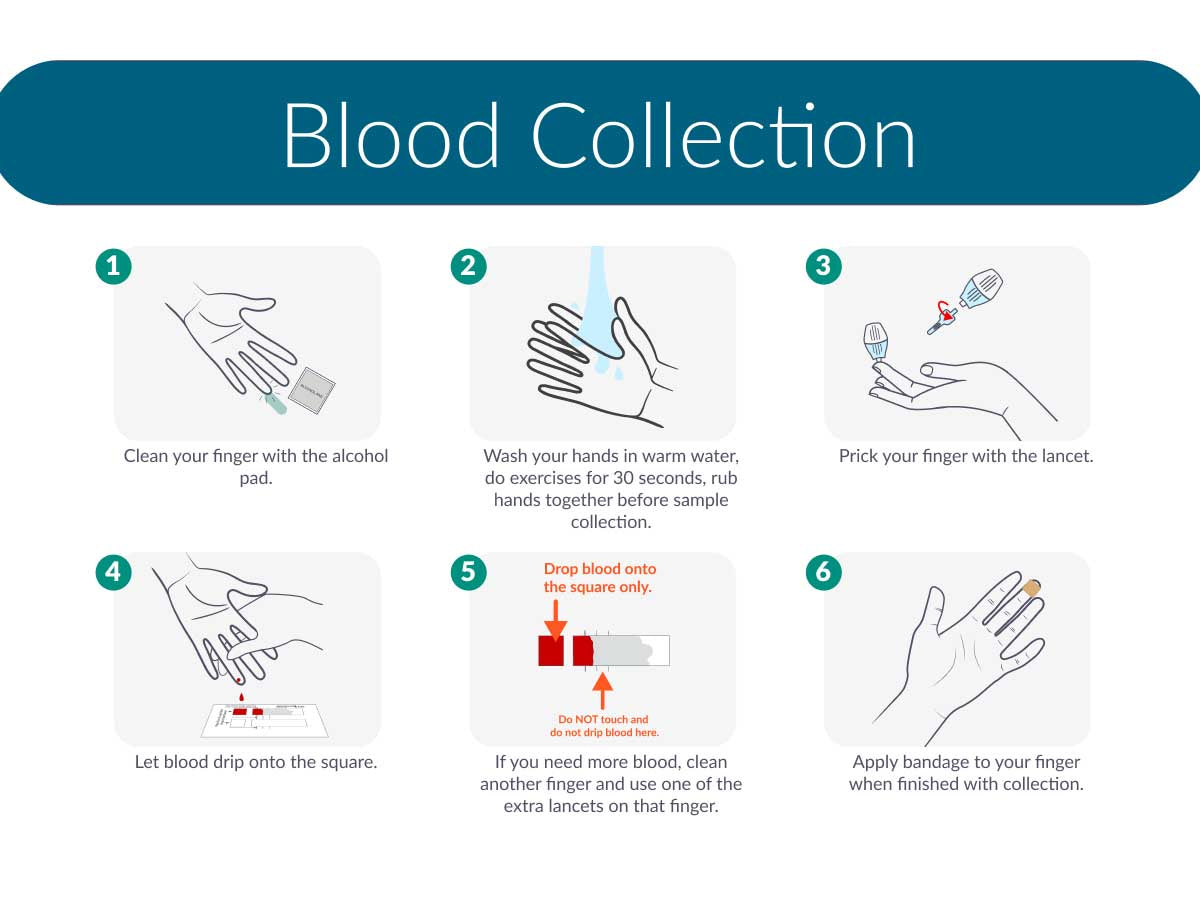
Register your test ID online and collect your sample:
Scan the QR code inside your kit and follow the instructions to collect your sample.
After collection:
- Let your sample dry completely on card (2 hours).
- Mail test box the same day using the prepaid label. If you take your test on Sunday, mail it in first thing on Monday.
Pre-Testing Video
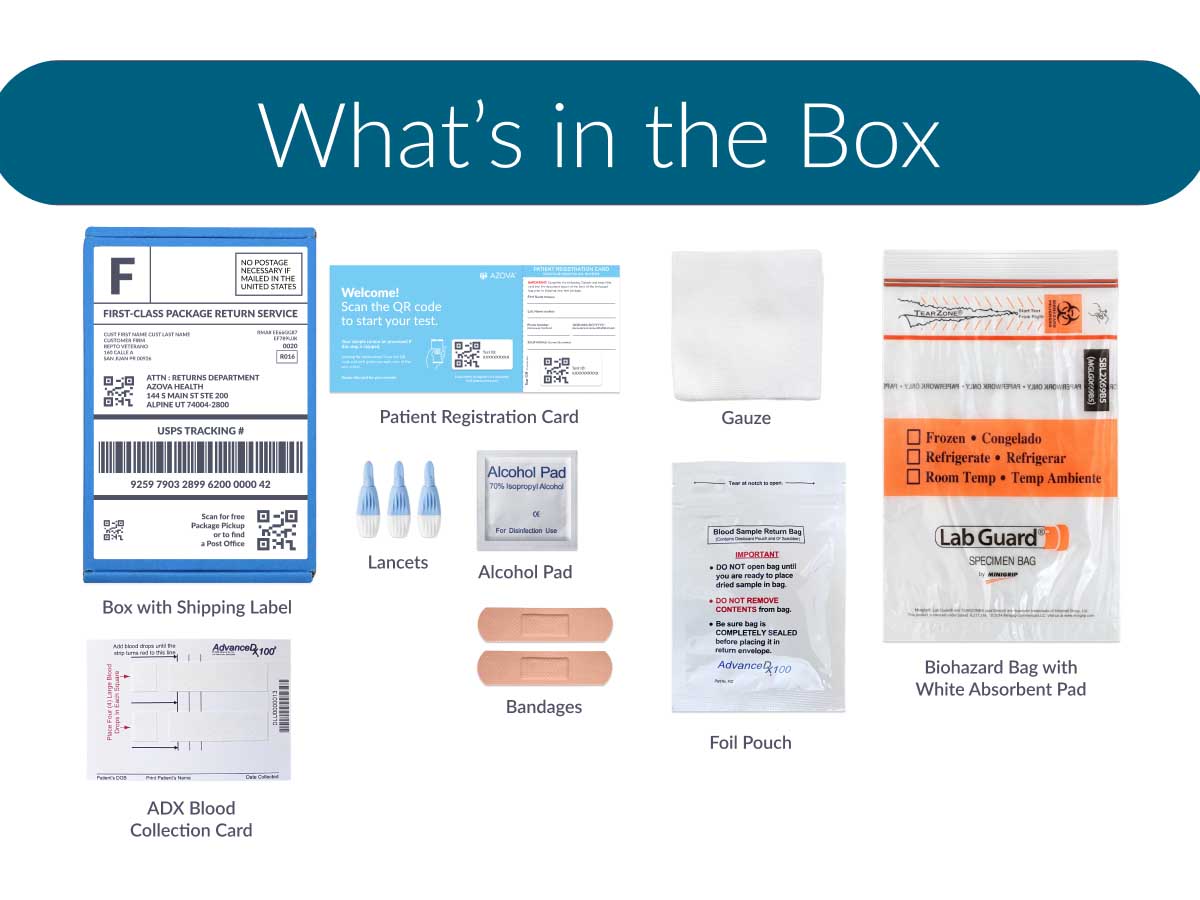
What is in the box?
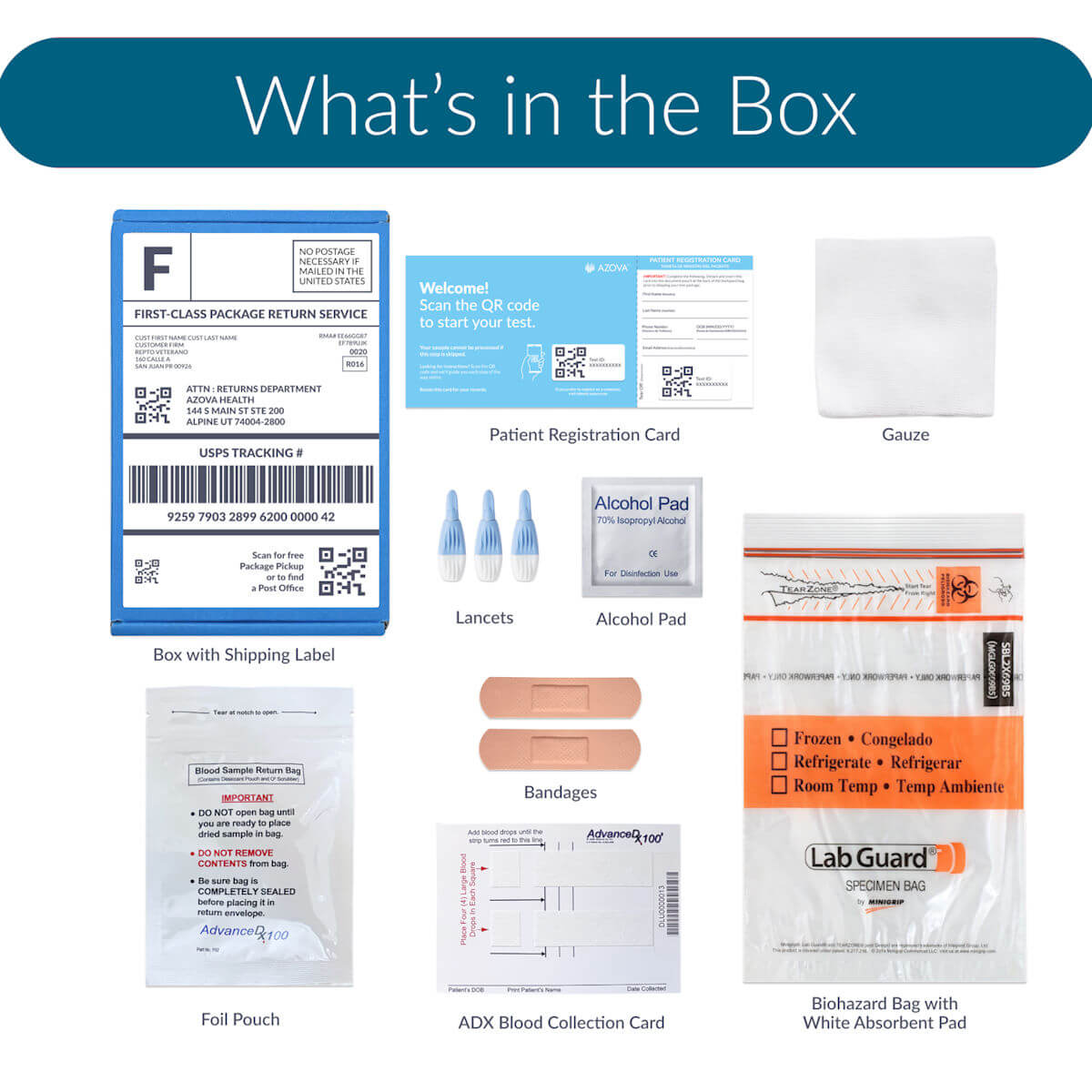
What to expect?
- Prepaid shipping label and packaging for an easy return to the lab
- All the necessary materials for sample collection
- Live 24/7/365 proctoring to guide you through the sample collection process
- Easy-to-follow video directions to help you along the way
- Digital (and printable) results found in the AZOVA app
The HEALTHBOX™
Liver and Expanded Lipids Test
Liver and Expanded Lipids Test
2-5 days
Couldn't load pickup availability





How it works
-
1
Collect your blood sample at home.
Fast and easy sample collection either with our online testing guide or virtual proctoring service.
-
2
Receive your results electronically.
Complete with a digital report that is printable in the AZOVA app.
-
3
Mail your sample to a CLIA-certified and CAP accredited lab.
You’ll receive an SMS and email notification when your sample arrives.
-
4
Take action on your results.
Access our educational materials or get a virtual care visit with a certified health provider (cost not included).
Frequently asked questions
Are AZOVA tests covered by FSA/HSA?
- Use your AZOVA test order confirmation to submit for FSA/HSA reimbursement.
- As defined by the IRS, many FSA/HSA benefits coordinators consider AZOVA tests to be qualified medical expenses.
- However, some FSA/HSA benefits coordinators might deny reimbursement. Before purchasing, please consider checking with your benefits coordinator to see if your FSA/HSA covers AZOVA products.
Who should take this test?
Adults age 18+ with chronic liver disease:
Conditions like hepatitis or fatty liver disease
Experiencing symptoms:
Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes), persistent abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, fatigue, and unexplained weight loss
On certain medications:
Doctor will set test frequency (monthly-6 months) to monitor liver function and adjust meds.
What if I have questions about this test or my results?
For questions about your test or results, contact AZOVA Customer Support at 844-692-9682, available 24/7.
For a more in-depth discussion of your results with a healthcare provider, AZOVA's Virtual Care is available at azova.com for an additional cost.
How often should I take this test?
If you're on liver-affecting medication, like Isotretinoin (Accutane and other brand names), your doctor will set test frequency, ranging from monthly to every 6 months, to help monitor and adjust your treatment.
In which states can I purchase this test?
Tests are available for individuals 18 years and older and require a blood sample. Availability of tests may vary by state. Visit azova.com/states for more information. This test is only intended for informational and educational use, and is not intended to be used for diagnostic purposes.
Purchase, registration, and use are subject to the AZOVA User Agreement available at azova.com/patient-terms.
Information presented here is not intended to diagnose or treat any condition and is provided for educational purposes only. Always consult with your healthcare provider before making any healthcare decisions.
If you are having a life threatening emergency, please call 911 immediately.

Virtual care 24/7
Save time and money when you see a doctor online.
Get started for $59.


Talk with Customer Support
You can call AZOVA’s Customer Support team for comprehensive support, including help with your account, testing, results and telemedicine visits.
Please note that wait times may vary depending on call volume.
(844) 692–9682








